Ethylene, C2H 4 , is a highly flammable, colorless and noncorrosive gas with a sweet odor. It is easily ignited and a flame can easily flash back to the source of the leak. Under prolonged exposure to fire or heat the containers may rupture violently and rocket. Can cause explosion. Vapors arising from the boiling liquid are lighter than air. Ethylene is not toxic, but is a simple asphyxiant.
Ethylene is used as an anesthetic, a refrigerant, and to make other chemicals as polymers and plastics.
Ethylene is produced in petrochemical processes, as steam cracking where hydrocarbons and steam are heated to 750–950 °C. This process converts large hydrocarbons into smaller ones and introduces unsaturated products.
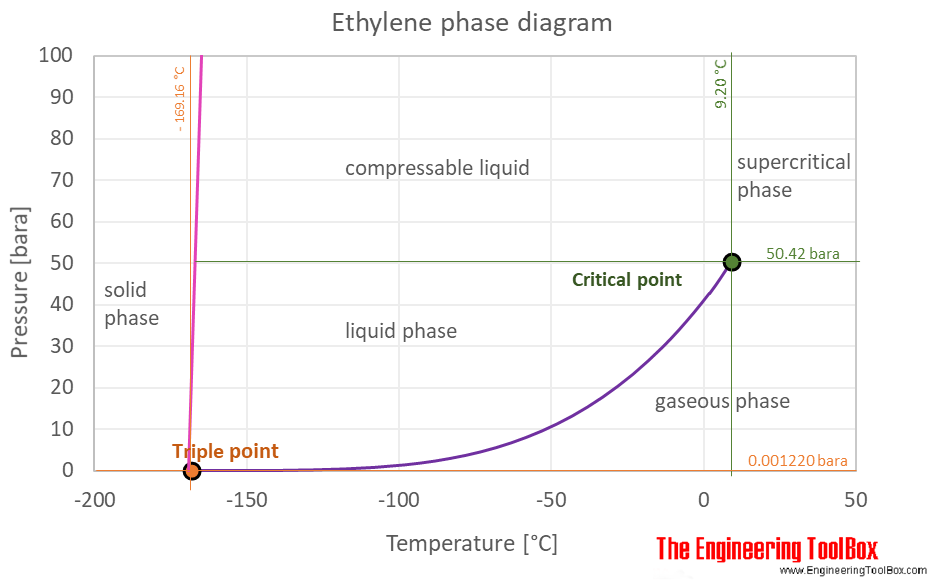
The phase diagram of ethylene is shown below the table.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of ethylene:
Values are given for gas phase at 25 o C /77 o F / 298 K and 1 bara, if not other phase, temperature or pressure given.
For full table with Imperial Units - rotate the screen!
| Property | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoignition temperature | 723 | K | 450 | °C | 842 | °F | ||
| Boiling Point | 169 | K | -104 | °C | -155 | °F | ||
| Critical density | 7.63 | mol/dm 3 | 214 | kg/m 3 | 0.415 | slug/ft 3 | 13.4 | lb/ft 3 |
| Critical pressure | 5.06 | MPa=MN/m 2 | 50.6 | bar | 49.9 | atm | 734 | psi=lbf /in 2 |
| Critical temperature | 282.4 | K | 9.2 | °C | 48.6 | °F | ||
| Critical volume | 131 | cm 3 /mol | 0.00467 | m 3 /kg | 2.41 | ft 3 /slug | 0.0748 | ft 3 /lb |
| Density | 40.6 | mol/m 3 | 1.138 | kg/m 3 | 0.00221 | slug/ft 3 | 0.07104 | lb/ft 3 |
| Density (liquid) at -104 °C/-155°F | 20567 | mol/m 3 | 577 | kg/m 3 | 1.12 | slug/ft 3 | 36.0 | lb/ft 3 |
| Flammable, gas and liquid | yes | highly | ||||||
| Flash point | 137 | K | -136 | °C | -213 | °F | ||
| Gas constant , individual, R | 296.4 | J/kg K | 0.0823 | Wh/(kg K) | 1772 | [ft lbf /slug °R] | 55.08 | [ft lbf /lb °R] |
| Gibbs free energy of formation (gas) | 68 | kJ/mol | 2424 | kJ/kg | 1042 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of combustion (gas) | -1411 | kJ/mol | -50303 | kJ/kg | -21626 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of formation (gas) | 52.4 | kJ/mol | 1868 | kJ/kg | 803 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat (enthalpy) of evaporation at -104°C/-155°F | 13.6 | kJ/mol | 483 | kJ/kg | 207.7 | Btu/lb | ||
| Heat capacity , Cp (gas) | 42.9 | J/mol K | 1.53 | kJ/kg K | 0.365 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | ||
| Heat capacity, Cp (liquid) at -104°C/-155°F | 67.4 | J/mol K | 2.40 | kJ/kg K | 0.574 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | ||
| Heat capacity, Cv (gas) | 34.6 | J/mol K | 1.24 | kJ/kg K | 0.295 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | ||
| Heat capacity, Cv (liquid) at -104°C/-155°F | 38.7 | J/mol K | 1.38 | kJ/kg K | 0.330 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | ||
| Ionization potential | 10.5 | eV | ||||||
| log K OW (Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient) | 1.13 | |||||||
| Melting point | 104.15 | K | -169.0 | °C | -272.2 | °F | ||
| Molecular Weight | 28.054 | g/mol | 0.06185 | lb/mol | ||||
| Solubility in water, at 25°C | 0.131 | mg/ml | ||||||
| Sound velocity | 330 | m/s | 1082 | ft/s | 739 | mi/h | ||
| Specific Gravity (gas) (relativ to air) | 0.978 | |||||||
| Specific Heat Ratio (gas) - CP /CV | 1.24 | |||||||
| Specific Heat Ratio (liquid) - CP /CV | 1.74 | |||||||
| Specific Volume | 0.0247 | m 3 /mol | 0.879 | m 3 /kg | 453 | ft 3 /slug | 14.1 | ft 3 /lb |
| Standard molar entropy , S° (gas) | 219.32 | J/mol K | 7.82 | kJ/kg K | 1.87 | Btu/lb °F | ||
| Standard molar entropy, S° (liquid) | 117.8 | J/mol K | 4.20 | kJ/kg K | 1.00 | Btu/lb °F | ||
| Surface tension at -104°C/-155°F | 16.00 | dynes/cm | 0.016 | N/m | ||||
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.020 | W/m°C | 0.0118 | Btu/hr ft °F | ||||
| Triple point pressure | 0.000122 | MPa=MN/m 2 | 0.00122 | bar | 0.00120 | atm | 0.0177 | psi=lbf /in 2 |
| Triple point temperature | 104.0 | K | -169.16 | °C | -272.49 | °F | ||
| Vapor (saturation) pressure | 6.9449 | MPa=MN/m 2 | 5.21E+04 | mm Hg | 68.543 | atm | 1007.30 | psi=lbf /in 2 |
| Viscosity , dynamic (absolute) | 0.0103 | cP | 6.9 | [lbm /ft s*10 -6 ] | 0.22 | [lbf s/ft 2 *10 -6 ] | ||
| Viscosity, kinematic | 9.05 | cSt | 97.4 | [ft 2 /s*10 -6 ] |
Follow the links below to get values for the listed properties of ethylene at varying pressure and temperature :
Ethylene is a gas at standard conditions. However, at low temperature and/or high pressures the gas becomes a liquid or a solid.
The ethylene phase diagram shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure. The curve between the critical point and the triple point shows the ethylene boiling point with changes in pressure. It also shows the saturation pressure with changes in temperature.

At the critical point there is no change of state when pressure is increased or if heat is added.
The triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.